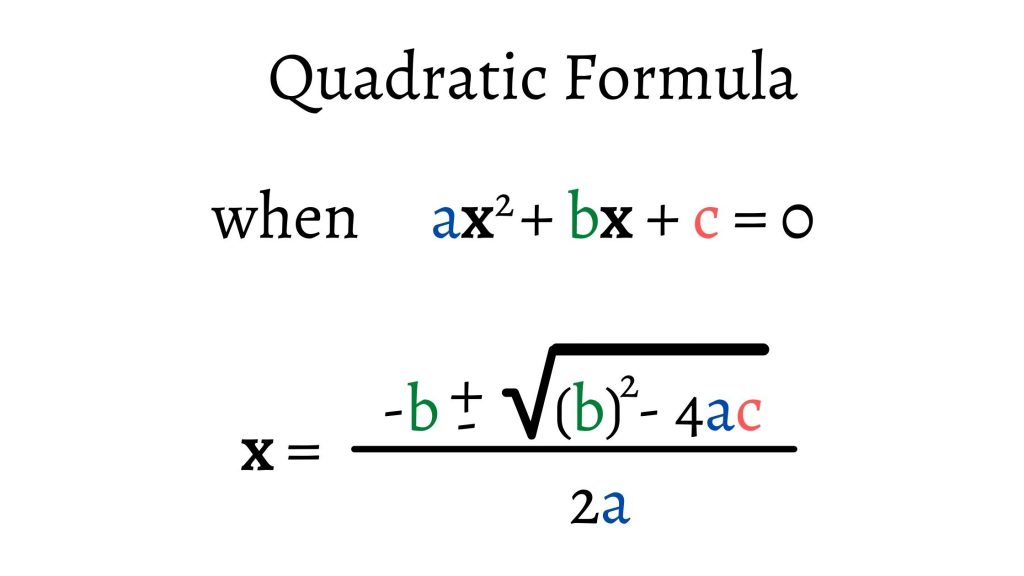Quadratic Function General Form
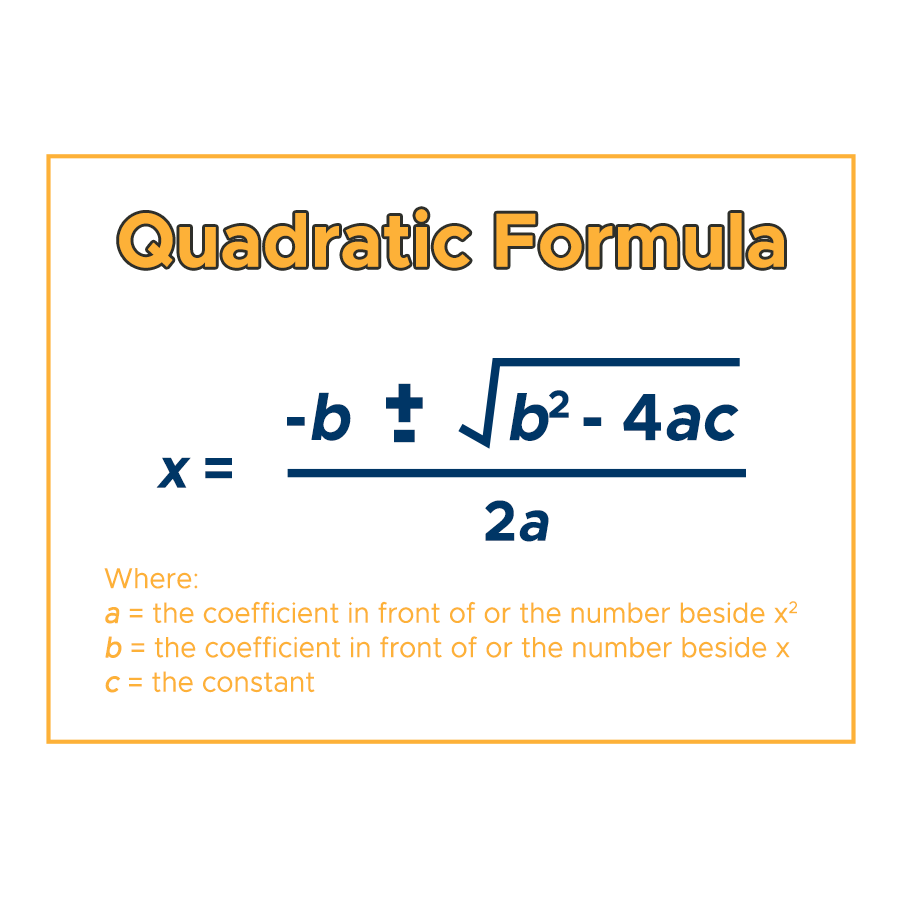
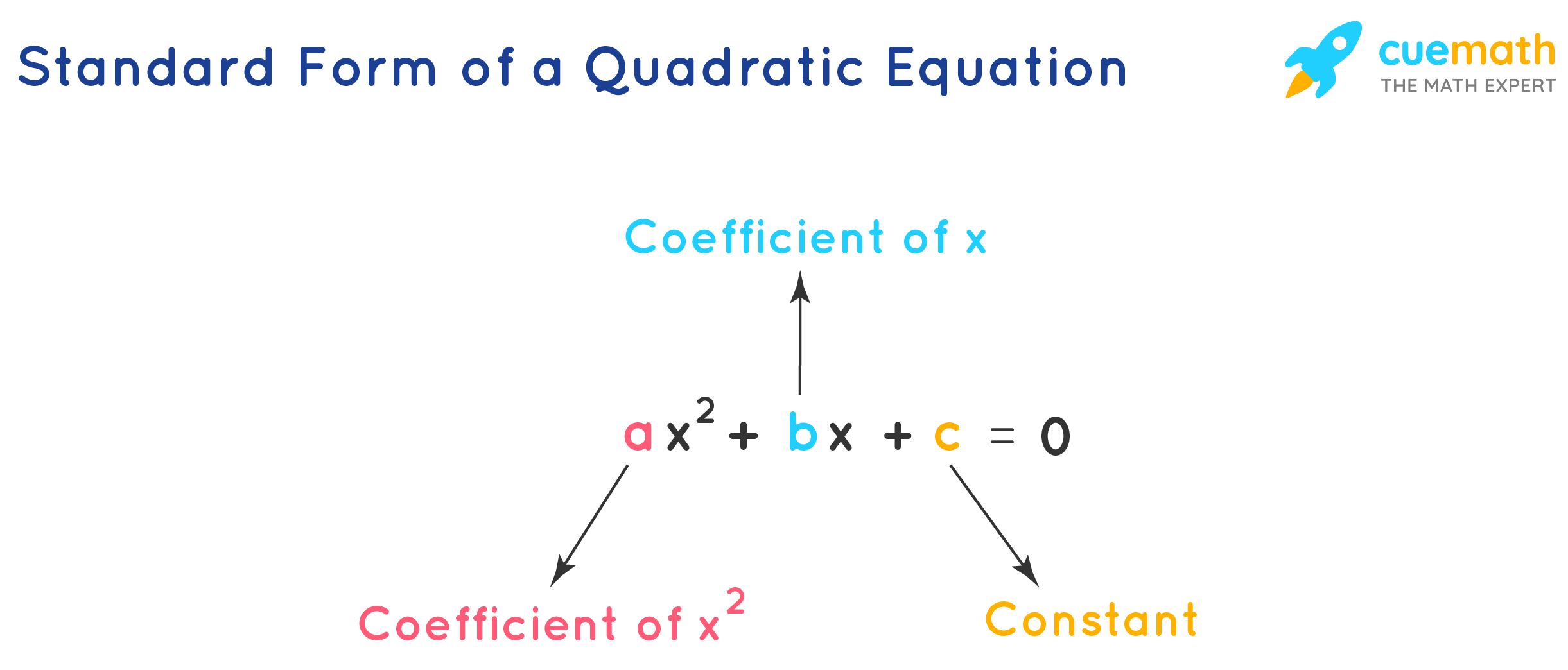
Quadratic Function General Form - In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.
Forms of a Quadratic Math Tutoring & Exercises
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
Quadratic Formula Equation & Examples Curvebreakers
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
Vertex Quadratic Equation Quadratic Equation
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
Quadratic Equation Presentation
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
Standard Form Quadratic Equation Here's What People Are Saying About
The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.
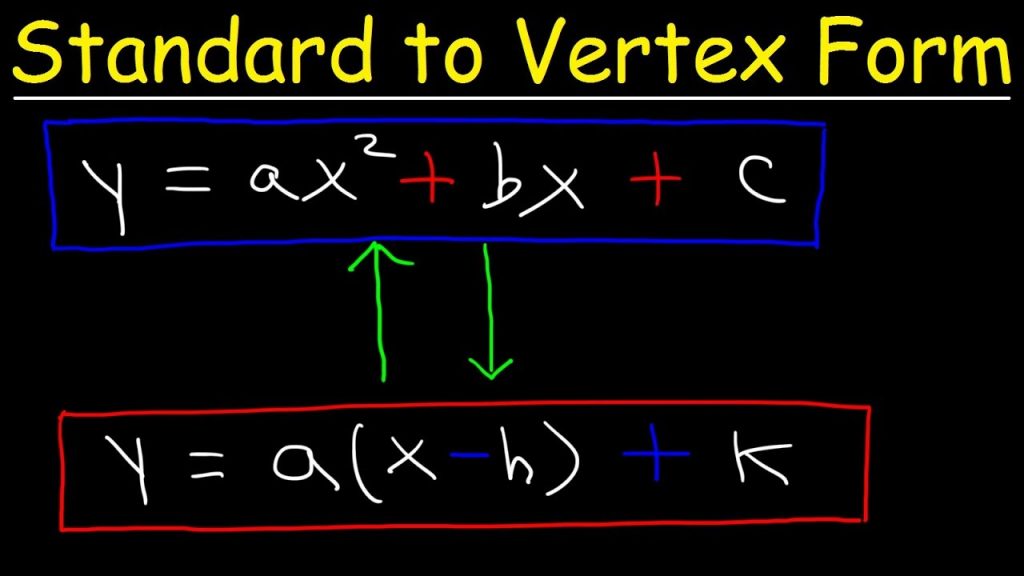
Different Forms of Quadratic Equation with Examples
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
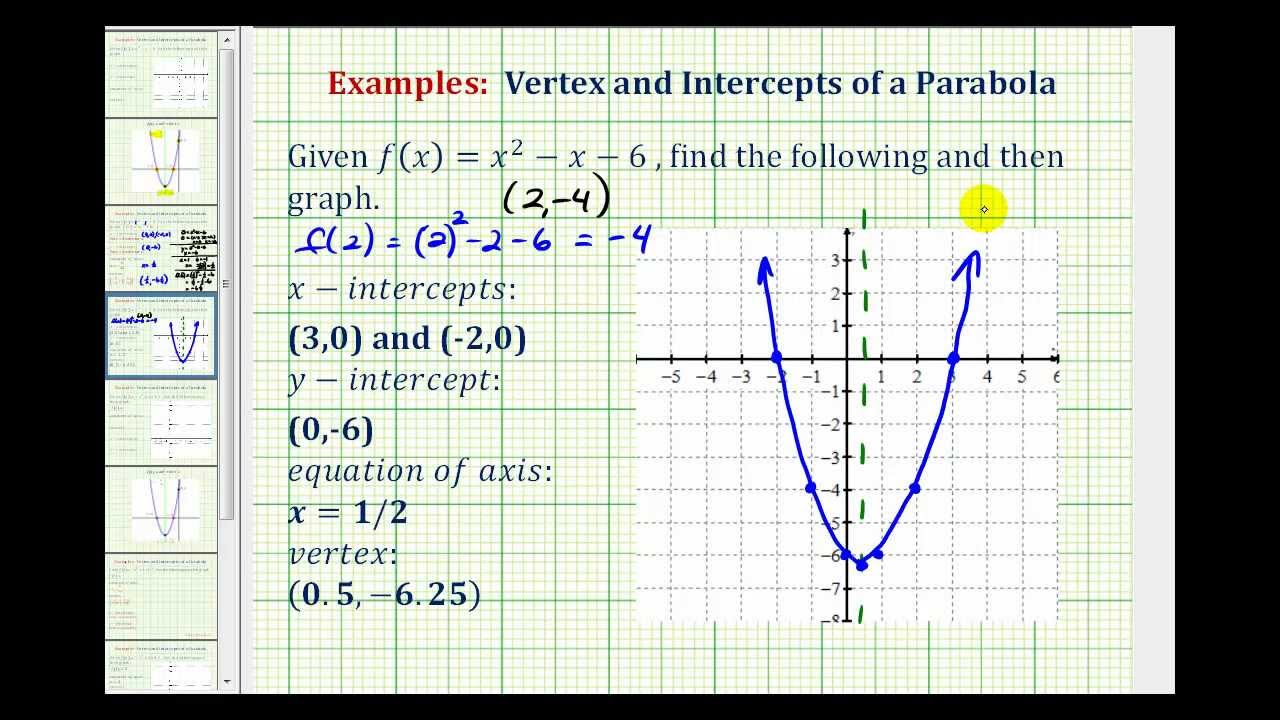
Ex1 Graph a Quadratic Function in General Form YouTube
The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.
General Form of Quadratic Equation SPM Additional Mathematics
The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.
Quadratic Equations Formulas, Methods, and Examples
The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.
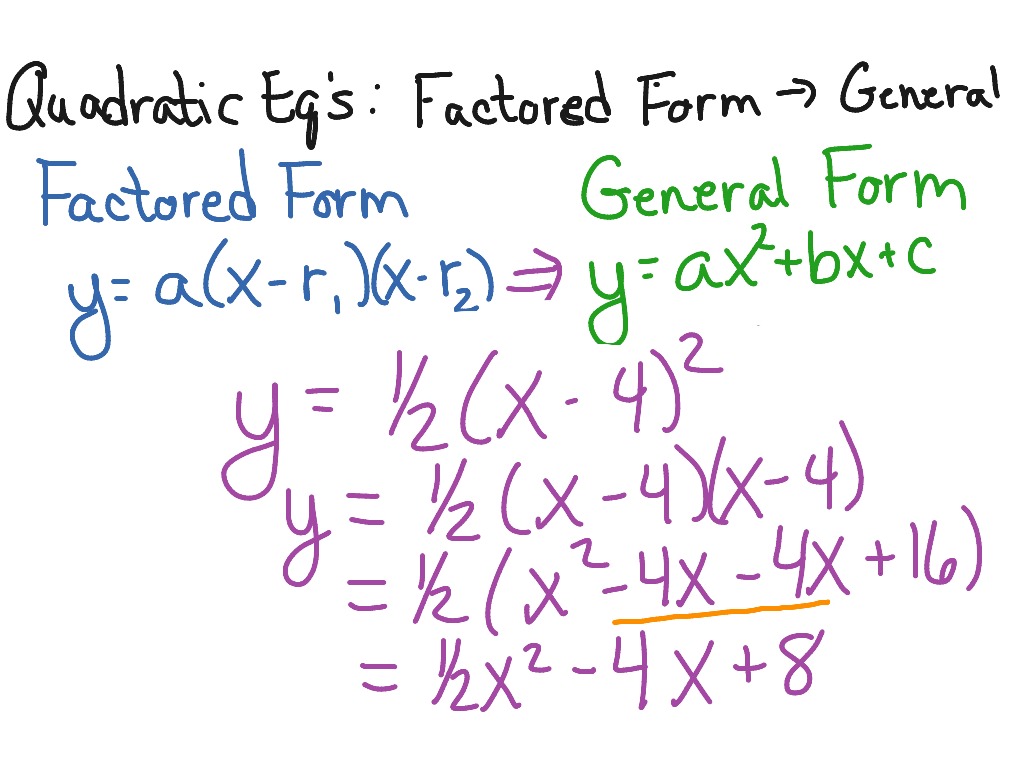
Quadratic Eq factored form to general form Math, Algebra, Quadratic
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The general form of a quadratic function is expressed as $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ where $a$, $b$, and $c$ are constants and $a \neq 0$.
The General Form Of A Quadratic Function Is Expressed As $Ax^2 + Bx + C = 0$ Where $A$, $B$, And $C$ Are Constants And $A \Neq 0$.
In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion.