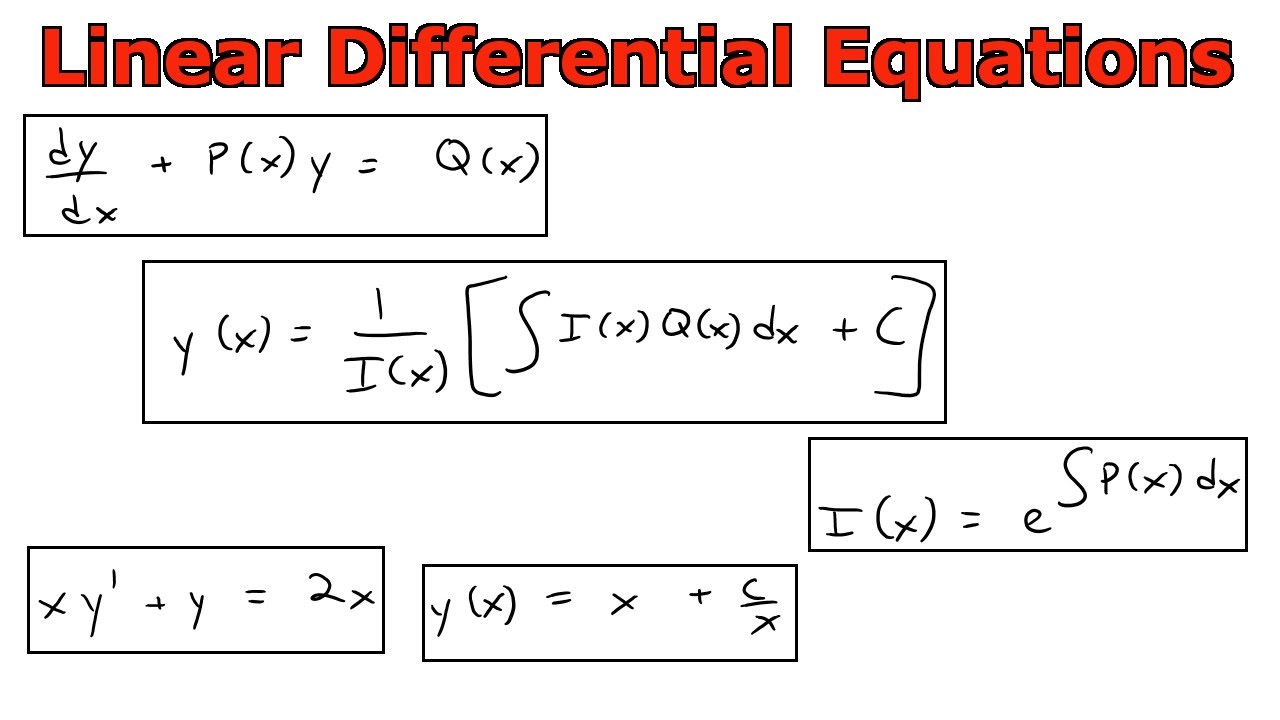
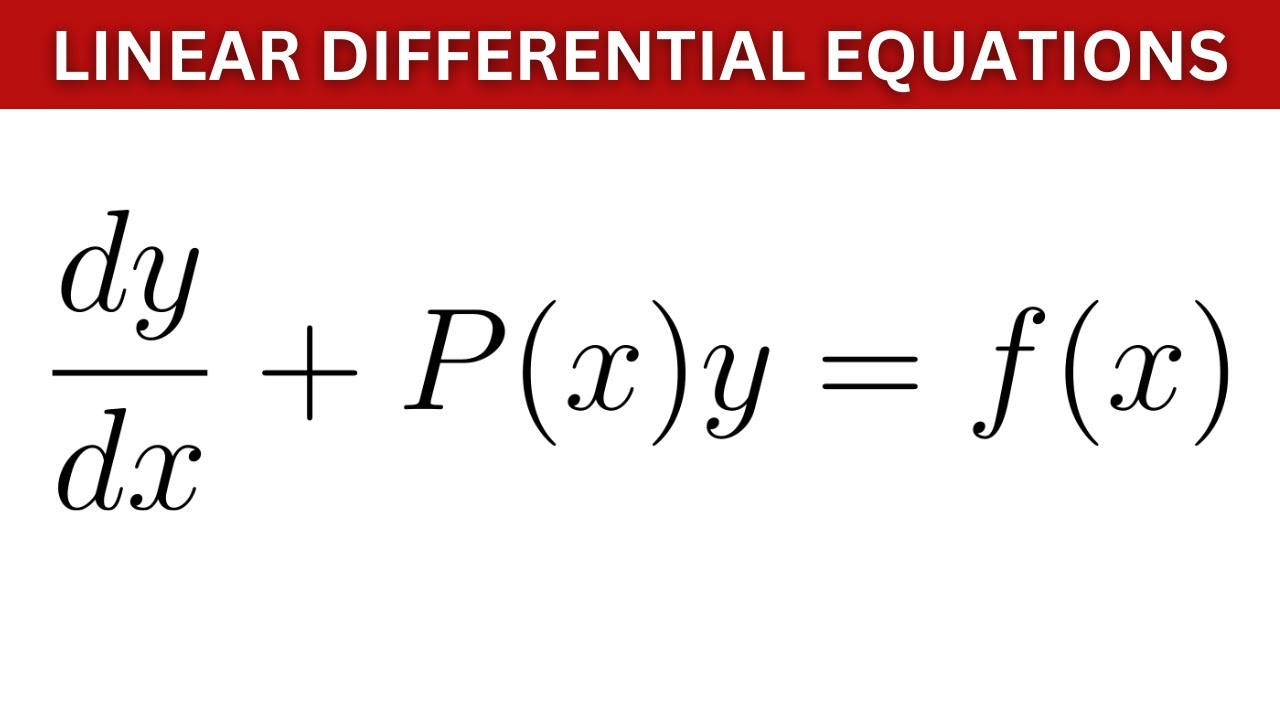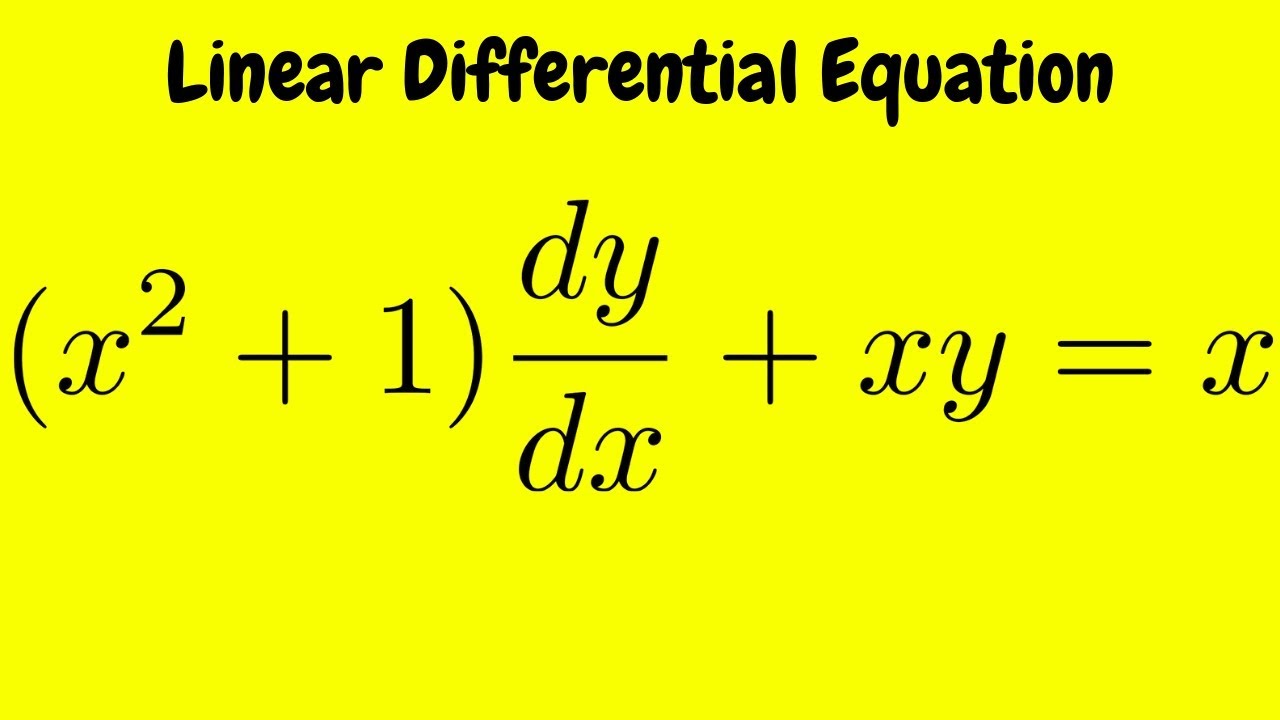Linear Form Differential Equation
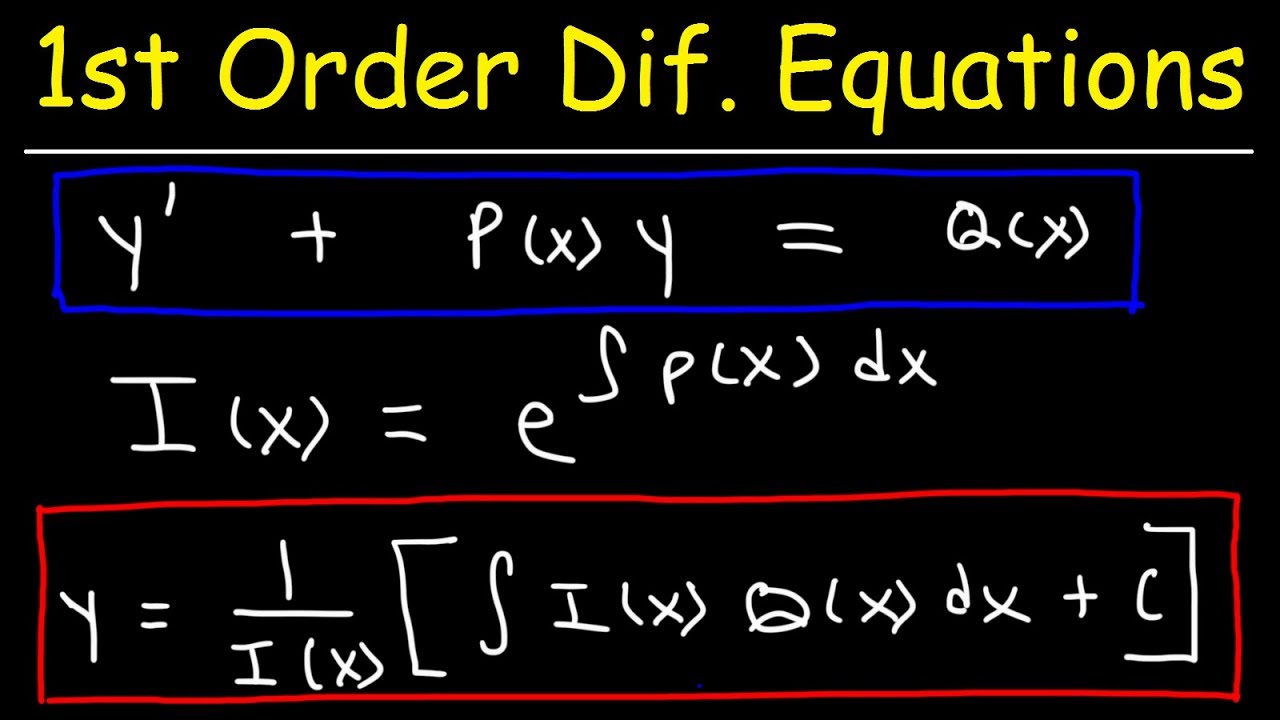
Linear Form Differential Equation - Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). We give an in depth. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. It consists of a y and a derivative. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz.
, etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). We give an in depth. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. It consists of a y and a derivative. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x.
It consists of a y and a derivative. State the definition of a linear differential equation. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. We give an in depth. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for.
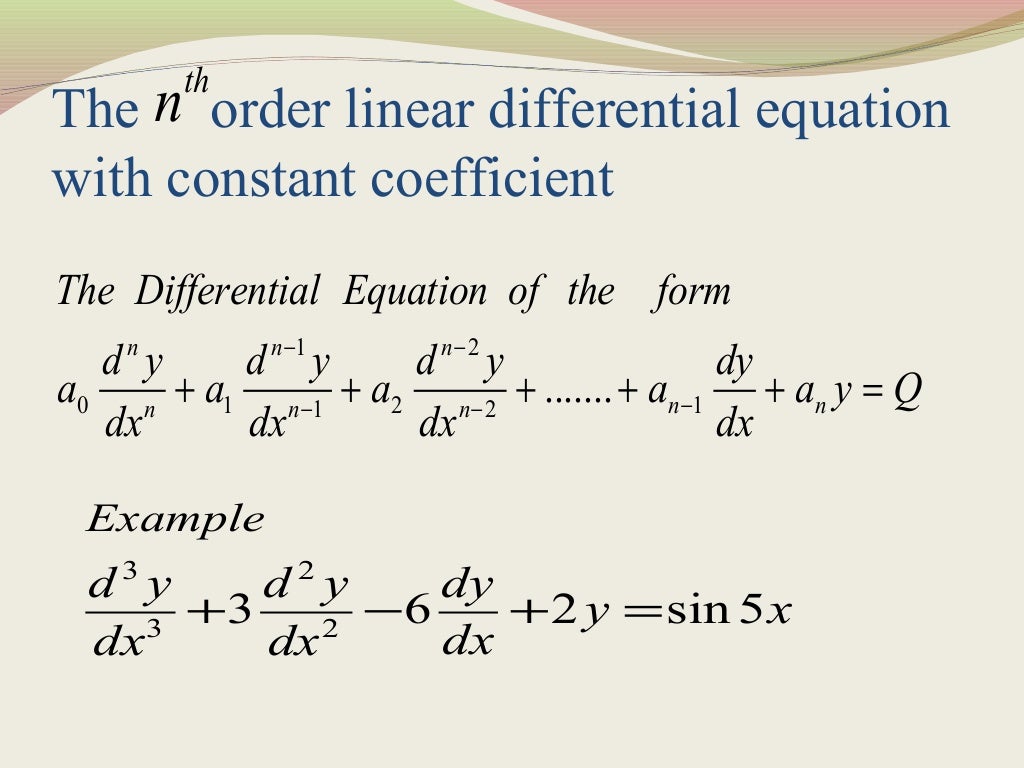
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). State the definition of a linear differential equation. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. It consists of a y and a derivative.
First Order Linear Differential Equations YouTube
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). It consists of a y and a derivative. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied.
Differential Equations (Definition, Types, Order, Degree, Examples)
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. State the definition of a linear differential equation. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. It consists of a y and a.
[Solved] In Chapter 6, you solved the firstorder linear differential
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. It consists of a y and a derivative. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. In.
Mathematics Class 12 NCERT Solutions Chapter 9 Differential Equations
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. State the definition.
Linear Differential Equations YouTube
It consists of a y and a derivative. State the definition of a linear differential equation. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations,.
Linear Differential Equations. Introduction and Example 1. YouTube
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. It consists of a y and a derivative.
Linear Differential Equations YouTube
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. We give an in depth. Differential equations in the form.
Solve the Linear Differential Equation (x^2 + 1)dy/dx + xy = x YouTube
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. In this section we solve linear first order differential.
Solving a First Order Linear Differential Equation YouTube
Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. We give an in depth. State the definition of a linear differential equation. , etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. It consists of a y and a derivative.
State The Definition Of A Linear Differential Equation.
, etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). A differential equation of the form =0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz.
In This Section We Solve Linear First Order Differential Equations, I.e.
Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations for. We give an in depth. It consists of a y and a derivative.